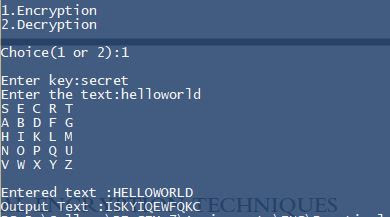
The Playfair cipher or Playfair square or Wheatstone-Playfair cipher is a manual symmetric encryption technique. The scheme was invented in 1854 by Charles Wheatstone, but bears the name of Lord Playfair for promoting its use.
The Playfair cipher uses a 5 by 5 table containing a key word or phrase. Memorization of the keyword and 4 simple rules was all that was required to create the 5 by 5 table and use the cipher.



0 comments:
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.